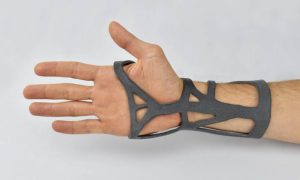
TPU is offering a really good shock absorption and rebound resilience (up to 63%). Thanks to its quality, high flexibility, TPU can be used to manufacture footwear, orthopedic models, and sports protection equipment. If you are looking for a resistant, flexible, and rubbery material, this TPU is the perfect option. By creating an interesting structural design, parts can be 3D printed for various applications in the medical sector.
Several TPU options, at Sculpteo we recommend: Ultrasint® TPU 88A for white parts, using Selective Laser Sintering technology, or Ultrasint® TPU01 for grey parts, using Multi Jet Fusion technology.
Nylon PA 11 is relevant for your medical projects. Indeed, this material is resistant and approved for skin contact, making it possible to create made-to-measure medical devices such as orthopedic parts.
If you want to use Nylon PA 11, two different options are available at Sculpteo, PA11 HP and Ultrasint® PA11.

The good mechanical properties of Nylon PA12 material can substitute injection molding plastics. This material is well used in the 3D printing industry, as it allows for rapid prototyping as well as finished consumer products. For medical, this material can be used to develop medical tools or prosthetics for example. Nylon PA12 is a biocompatible and sterilizable 3D printing material that makes it a relevant material to develop your medical projects.


 Connect with Google
Connect with Google Connect with Facebook
Connect with Facebook