The 3D printing revolution has influenced some industries’ operations. Here is how it is changing some fields.
Impact on the architecture industry
Housing prices have been increasing over the past few years, but an emerging housing solution aims to counter this and simplify the procedure of acquiring a house. This technology is still experimental; hence, it might take a while to become widespread and disrupt the construction industry. Using 3D printing technology to build houses has the potential to change the industry by enabling construction companies to construct houses quickly and efficiently. Traditional building methods are often time-consuming and labour-intensive. Some construction companies are testing this printing technology and have been able to construct entire buildings in a few days or weeks, making it a viable option for many real estate developers. However, workers must complete the buildings by adding and joining elements like roofs, windows and doors.
Additive fabrication also allows for greater customization in real estate construction because architects and builders can quickly create custom designs for their clients using 3D modelling software. They can promptly print out their designs’ models, allowing clients to visualize the final product before construction begins. By doing this, they enhance customer satisfaction and help streamline the design process.
Impact on the automotive industry
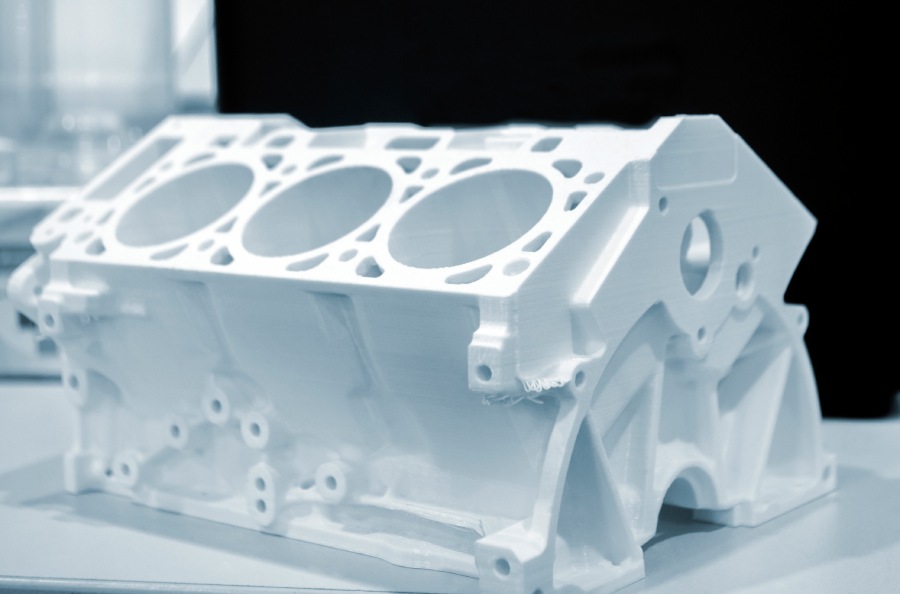
As the automotive industry moves towards a new age of electric vehicles and greater emphasis on sustainability, the competition to produce quality vehicles profitably remains fiercely challenging. Manufacturers constantly seek tools and technologies to help them balance efficiency, lean manufacturing, production costs, sustainability and agile design processes while meeting strict quality requirements. Additive manufacturing has become a vital tool for automotive manufacturers in achieving this delicate balance. It has revolutionized the industry, increasing efficiency and improving product development.
Additive manufacturing has had a big impact on the rapid prototyping of new features for future vehicles. Legacy prototyping methods such as machining and injection moulding are too expensive and time-consuming, whereas additive fabrication allows for prototypes’ cost-effectiveness and quick creation. The technique lets automotive corporations frequently develop and test automobile components, leading to more efficient and effective product development operations.
Furthermore, additive manufacturing supports the creation of complex, organic shapes for applications like bodywork components for race cars. It also enables the creation of highly customized parts, which is essential in automotive manufacturing. The technology also helps reduce the weight of vehicles by utilizing lightweight materials such as engineered plastics and composites, leading to improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. It also contributes to the overall sustainability of the manufacturing process by reducing waste and allowing the usage of environmentally friendly materials.
Finally, additive fabrication facilitates the on-demand production of automotive parts, eliminating the need for large spare parts inventories and reducing stock-out risk. Car collectors can also use additive manufacturing techniques to print spare parts for vintage cars. In most cases, manufacturers discontinue the production of the required replacement parts and charge collectors a lot of money to replace them.
Impacts on the medical industry
The medical world has seen many innovations that have improved people’s lives. Hospitals have been able to create components like artificial limbs, parts of the skull and dental implants. Some hospitals have set up departments that design and create these components. Prosthetics have become advanced but are expensive to acquire and replace if damaged. A cosmetic prosthetic arm can cost over 4,500 US Dollars, and the buyer must pay an extra 6,000 if they want one with split hooks. Prosthetics with more advanced features can cost over 19,000 US Dollars, making them unattainable for people in underdeveloped countries. Additive fabrication has enabled people to collaborate and develop customizable prosthetic designs for hands and arms. Consequently, the end price of these products has become significantly cheaper. They can go for as low as 100 US Dollars, letting disabled people buy and modify them as their bodies change and grow.
Several people have surgeries to get implants to replace body parts like hips, joints, knees and spine fragments. Future innovations hold the potential to improve the quality of 3D-printed parts by allowing them to be customized to suit the patient. Doctors can study and practice with printed models before surgery, potentially improving the surgery’s result. Researchers are also working on bioprinting organs for patients that need organ donations. However, the challenge of creating complex organs is that they need blood and oxygen to function. In addition, organs and blood vessels have to be printed at the same time. A completed organ must be compatible with the patient’s body so that it does not reject them.


 Connect with Google
Connect with Google Connect with Facebook
Connect with Facebook